Here we’ll introduce the case of 2D bifurcation flow with parabolic inflow boundary condition.
Example 14: 2D bifurcation flow
The parameter definition of the case of 2D bifurcation flow is shown in the figure, where the inlet fluid velocity varies periodically.
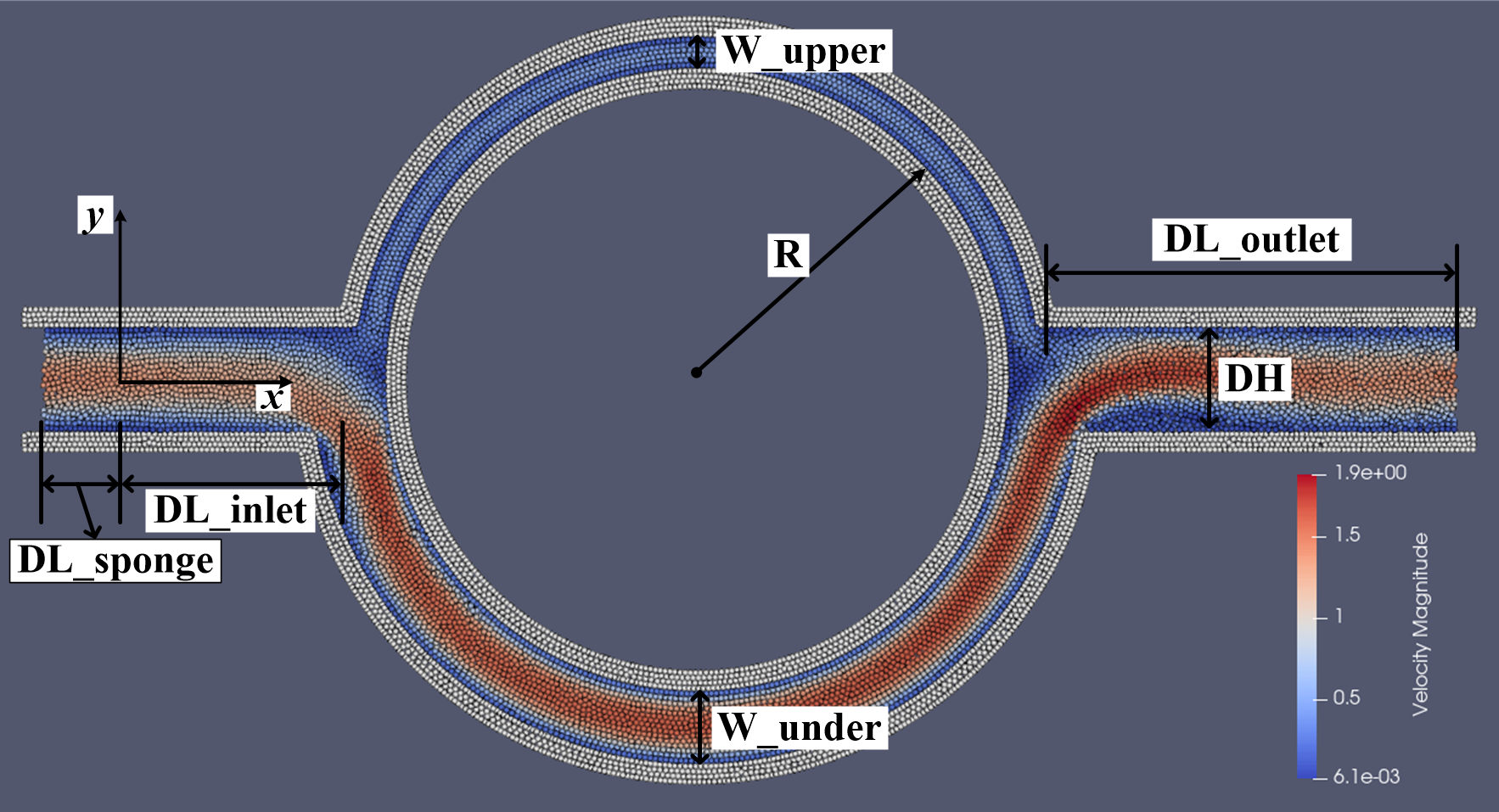
The distribution of the velocity magnititude and parameter definition.
First, we provide the following program to create a system for this problem.
/**
* @file test_2d_bifurcation_flow.cpp
* @brief This is the benchmark test for the bifurcation flow.
* @author Dong Wu
*/
/**
* @brief SPHinXsys Library.
*/
#include "sphinxsys.h"
/**
* @brief Namespace cite here.
*/
using namespace SPH;
/**
* @brief Basic geometry parameters.
*/
Real DL_inlet = 4.0; /**< Inlet channel length. */
Real DL_outlet = 8.0; /**< Outlet channel length. */
Real DH = 2.0; /**< Inlet and outlet channel height. */
Real R = 4.0; /**< Branch radius. */
Real W_upper = 0.8; /**< Upper branch width. */
Real W_under = 1.2; /**< Under branch width. */
Real N = 180; /**< Particle number for creating branch. */
Vec2d insert_circle_center(DL_inlet + R + W_upper, 0.0); /**< Location of the branch center. */
Real resolution_ref = 0.1; /**< Global reference resolution. */
Real DL_sponge = resolution_ref * 20.0; /**< Sponge region to impose inflow condition. */
Real BW = resolution_ref * 4.0; /**< Boundary width, determined by specific layer of boundary particles. */
/** Domain bounds of the system. */
BoundingBox system_domain_bounds(Vec2d(-DL_sponge - BW, -R - W_under - BW),
Vec2d(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, R + W_upper + BW));
/**
* @brief Material properties of the fluid.
*/
Real rho0_f = 1.0; /**< Density. */
Real U_f = 1.0; /**< Characteristic velocity. */
Real c_f = 10.0 * U_f; /**< Speed of sound. */
Real Re = 100.0; /**< Reynolds number. */
Real mu_f = rho0_f * U_f * DH / Re; /**< Dynamics viscosity. */
/**
* @brief define geometry of SPH bodies
*/
/** create a water block shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape1()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape1;
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, 0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper), 0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper), -0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
return water_block_shape1;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape2()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape2;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
water_block_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] + (R + W_upper) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
water_block_shape2.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet, 0.0));
return water_block_shape2;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape3()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape3;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
water_block_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + (R + W_under) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] - (R + W_under) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
water_block_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + R + W_under, 0.0));
return water_block_shape3;
}
/** create a water block buffer shape. */
MultiPolygon createInflowBufferShape()
{
std::vector<Vecd> inflow_buffer_shape;
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, 0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(0.0, 0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(0.0, -0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(inflow_buffer_shape, ShapeBooleanOps::add);
return multi_polygon;
}
/** create outer wall shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape1()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape1;
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, 0.5 * DH + BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, 0.5 * DH + BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
return outer_wall_shape1;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape2()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape2;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
outer_wall_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper + BW) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] + (R + W_upper + BW) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
outer_wall_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper + BW), 0.0));
return outer_wall_shape2;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape3()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape3;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
outer_wall_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + (R + W_under + BW) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] - (R + W_under + BW) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
outer_wall_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + R + W_under + BW, 0.0));
return outer_wall_shape3;
}
/** create inner wall shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createInnerWallShape()
{
std::vector<Vecd> inner_wall_shape;
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, 0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, 0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, -0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH ));
return inner_wall_shape;
}
/** Fluid body definition */
class WaterBlock : public FluidBody
{
public:
WaterBlock(SPHSystem& system, std::string body_name)
: FluidBody(system, body_name)
{
/** Geomtry definition. */
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape1(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
body_shape_.add<MultiPolygonShape>(multi_polygon);
}
};
/* Definition of the solid body. */
class WallBoundary : public SolidBody
{
public:
WallBoundary(SPHSystem& system, std::string body_name)
: SolidBody(system, body_name, makeShared<SPHAdaptation>(1.15, 1.0))
{
/** Geomtry definition. */
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape1(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createInnerWallShape(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R - BW, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
MultiPolygonShape multi_polygon_shape(multi_polygon);
body_shape_.add<LevelSetShape>(this, multi_polygon_shape);
}
};
/** Case dependent inflow boundary condition. */
class ParabolicInflow : public fluid_dynamics::InflowBoundaryCondition
{
Real u_ave_, u_ref_, t_ref;
public:
ParabolicInflow(FluidBody &fluid_body, BodyPartByCell &constrained_region)
: InflowBoundaryCondition(fluid_body, constrained_region),
u_ave_(0), u_ref_(1.0), t_ref(20.0) {}
Vecd getTargetVelocity(Vecd& position, Vecd& velocity)
{
Real u = velocity[0];
Real v = velocity[1];
if (position[0] < 0.0) {
u = (-6.0 * position[1] * position[1] / DH / DH + 1.5) * u_ave_;
v = 0.0;
}
return Vecd(u, v);
}
void setupDynamics(Real dt = 0.0) override
{
Real run_time = GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_;
u_ave_ = u_ref_ * 0.5 * (1.0 + sin(Pi * run_time / t_ref - 0.5 * Pi));
}
};
/** fluid observer particle generator */
class FluidObserverParticleGenerator : public ParticleGeneratorDirect
{
public:
FluidObserverParticleGenerator() : ParticleGeneratorDirect()
{
/** A line of measuring points at the entrance of the channel. */
size_t number_observation_pionts = 21;
Real range_of_measure = DH - resolution_ref * 4.0;
Real start_of_measure = resolution_ref * 2.0 - 0.5 * DH;
/** the measureing particles */
for (size_t i = 0; i < number_observation_pionts; ++i)
{
Vec2d point_coordinate(0.0, range_of_measure * Real(i) / Real(number_observation_pionts - 1) + start_of_measure);
positions_volumes_.push_back(std::make_pair(point_coordinate, 0.0));
}
}
};
/** Main program starts here. */
int main(int ac, char* av[])
{
/** Build up the environment of a SPHSystem with global controls. */
SPHSystem system(system_domain_bounds, resolution_ref);
/** Tag for run particle relaxation for the initial body fitted distribution. */
system.run_particle_relaxation_ = false;
/** Tag for computation start with relaxed body fitted particles distribution. */
system.reload_particles_ = true;
/** Tag for computation from restart files. 0: start with initial condition. */
system.restart_step_ = 0;
//handle command line arguments
#ifdef BOOST_AVAILABLE
system.handleCommandlineOptions(ac, av);
#endif
/** output environment. */
In_Output in_output(system);
/**
* @brief Creating body, materials and particles.
*/
WaterBlock water_block(system, "WaterBody");
FluidParticles fluid_particles(water_block, makeShared<WeaklyCompressibleFluid>(rho0_f, c_f, mu_f));
WallBoundary wall_boundary(system, "Wall");
SharedPtr<ParticleGenerator> wall_particle_generator = makeShared<ParticleGeneratorLattice>();
if (!system.run_particle_relaxation_ && system.reload_particles_)
wall_particle_generator = makeShared<ParticleGeneratorReload>(in_output, wall_boundary.getBodyName());
SolidParticles wall_particles(wall_boundary, wall_particle_generator);
ProbeBody fluid_observer(system, "FluidObserver");
ObserverParticles flow_observer_particles(fluid_observer, makeShared<FluidObserverParticleGenerator>());
/**
* @brief Define body relation map.
* The contact map gives the topological connections between the bodies.
* Basically the the range of bodies to build neighbor particle lists.
*/
BodyRelationInner water_block_inner(water_block);
ComplexBodyRelation water_block_complex(water_block, { &wall_boundary });
BodyRelationContact fluid_observer_contact(fluid_observer, { &water_block });
/** Run particle relaxation for body-fitted distribution if chosen. */
if (system.run_particle_relaxation_)
{
/** body topology only for particle relaxation */
BodyRelationInner wall_boundary_inner(wall_boundary);
/**
* @brief Methods used for particle relaxation.
*/
/** Random reset the particle position. */
RandomizePartilePosition random_wall_boundary_particles(wall_boundary);
/** Write the body state to Vtu file. */
BodyStatesRecordingToVtp write_wall_boundary_to_vtp(in_output, { &wall_boundary });
/** Write the particle reload files. */
ReloadParticleIO write_wall_boundary_particle_reload_files(in_output, { &wall_boundary });
/** A Physics relaxation step. */
relax_dynamics::RelaxationStepInner relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner(wall_boundary_inner);
/**
* @brief Particle relaxation starts here.
*/
random_wall_boundary_particles.parallel_exec(0.25);
relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner.surface_bounding_.parallel_exec();
write_wall_boundary_to_vtp.writeToFile(0);
/** relax particles of the insert body. */
int ite_p = 0;
while (ite_p < 1000)
{
relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner.parallel_exec();
ite_p += 1;
if (ite_p % 200 == 0)
{
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(9) << "Relaxation steps for the inserted body N = " << ite_p << "\n";
write_wall_boundary_to_vtp.writeToFile(ite_p);
}
}
std::cout << "The physics relaxation process of the cylinder finish !" << std::endl;
/** Output results. */
write_wall_boundary_particle_reload_files.writeToFile(0);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief Methods used for time stepping.
*/
/** Initialize particle acceleration. */
TimeStepInitialization initialize_a_fluid_step(water_block);
/** Evaluation of density by summation approach. */
fluid_dynamics::DensitySummationComplex update_density_by_summation(water_block_complex);
/** Time step size without considering sound wave speed. */
fluid_dynamics::AdvectionTimeStepSize get_fluid_advection_time_step_size(water_block, U_f);
/** Time step size with considering sound wave speed. */
fluid_dynamics::AcousticTimeStepSize get_fluid_time_step_size(water_block);
/** Pressure relaxation using verlet time stepping. */
/** Here, we do not use Riemann solver for pressure as the flow is viscous. */
fluid_dynamics::PressureRelaxationWithWall pressure_relaxation(water_block_complex);
fluid_dynamics::DensityRelaxationRiemannWithWall density_relaxation(water_block_complex);
/** Computing viscous acceleration. */
fluid_dynamics::ViscousAccelerationWithWall viscous_acceleration(water_block_complex);
/** Impose transport velocity. */
fluid_dynamics::TransportVelocityCorrectionComplex transport_velocity_correction(water_block_complex);
/** viscous acceleration and transport velocity correction can be combined because they are independent dynamics. */
CombinedInteractionDynamics viscous_acceleration_and_transport_correction(viscous_acceleration, transport_velocity_correction);
/** Computing vorticity in the flow. */
fluid_dynamics::VorticityInner compute_vorticity(water_block_inner);
/** Inflow boundary condition. */
MultiPolygonShape inflow_buffer_shape(createInflowBufferShape());
BodyRegionByCell inflow_buffer(water_block, "Buffer", inflow_buffer_shape);
ParabolicInflow parabolic_inflow(water_block, inflow_buffer);
/** Periodic BCs in x direction. */
PeriodicConditionInAxisDirectionUsingCellLinkedList periodic_condition(water_block, xAxis);
/**
* @brief Define the methods for I/O operations and observations of the simulation.
*/
BodyStatesRecordingToVtp write_real_body_states(in_output, system.real_bodies_);
RestartIO restart_io(in_output, system.real_bodies_);
ObservedQuantityRecording<Vecd>
write_fluid_velocity("Velocity", in_output, fluid_observer_contact);
/**
* @brief Prepare the simulation with cell linked list, configuration
* and case specified initial condition if necessary.
*/
/** initialize cell linked lists for all bodies. */
system.initializeSystemCellLinkedLists();
/** periodic condition applied after the mesh cell linked list build up
* but before the configuration build up. */
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
/** initialize configurations for all bodies. */
system.initializeSystemConfigurations();
/** computing surface normal direction for the wall. */
wall_particles.initializeNormalDirectionFromBodyShape();
/**
* @brief Load restart file if necessary.
*/
if (system.restart_step_ != 0)
{
GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ = restart_io.readRestartFiles(system.restart_step_);
water_block.updateCellLinkedList();
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
/** one need update configuration after periodic condition. */
water_block_complex.updateConfiguration();
}
/**
* @brief Setup for time-stepping control
*/
size_t number_of_iterations = system.restart_step_;
int screen_output_interval = 100;
int restart_output_interval = screen_output_interval * 10;
Real End_Time = 100.0; /**< End time. */
Real D_Time = End_Time / 100.0; /**< time stamps for output. */
Real Dt = 0.0; /**< Default advection time step sizes for fluid. */
Real dt = 0.0; /**< Default acoustic time step sizes for fluid. */
size_t inner_ite_dt = 0;
/** Statistics for computing time. */
tick_count t1 = tick_count::now();
tick_count::interval_t interval;
/** First output before the main loop. */
write_real_body_states.writeToFile();
write_fluid_velocity.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
/**
* @brief Main loop starts here.
*/
while (GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ < End_Time)
{
Real integration_time = 0.0;
/** Integrate time (loop) until the next output time. */
while (integration_time < D_Time)
{
initialize_a_fluid_step.parallel_exec();
Dt = get_fluid_advection_time_step_size.parallel_exec();
update_density_by_summation.parallel_exec();
viscous_acceleration_and_transport_correction.parallel_exec(Dt);
inner_ite_dt = 0;
Real relaxation_time = 0.0;
while (relaxation_time < Dt)
{
dt = SMIN(get_fluid_time_step_size.parallel_exec(), Dt);
/** Fluid pressure relaxation */
pressure_relaxation.parallel_exec(dt);
/** Fluid density relaxation */
density_relaxation.parallel_exec(dt);
relaxation_time += dt;
integration_time += dt;
GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ += dt;
parabolic_inflow.parallel_exec();
inner_ite_dt++;
}
if (number_of_iterations % screen_output_interval == 0)
{
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(9) << "N=" << number_of_iterations << " Time = "
<< GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_
<< " Dt = " << Dt << " Dt / dt = " << inner_ite_dt << "\n";
if (number_of_iterations % restart_output_interval == 0 && number_of_iterations != system.restart_step_)
restart_io.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
}
number_of_iterations++;
/** Water block configuration and periodic condition. */
periodic_condition.bounding_.parallel_exec();
water_block.updateCellLinkedList();
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
water_block_complex.updateConfiguration();
}
tick_count t2 = tick_count::now();
/** write run-time observation into file */
compute_vorticity.parallel_exec();
write_real_body_states.writeToFile();
fluid_observer_contact.updateConfiguration();
write_fluid_velocity.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
tick_count t3 = tick_count::now();
interval += t3 - t2;
}
tick_count t4 = tick_count::now();
tick_count::interval_t tt;
tt = t4 - t1 - interval;
std::cout << "Total wall time for computation: " << tt.seconds() << " seconds." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Let’s go through the program line by line and see how it works. It begins with the include statement:
/**
* @file test_2d_bifurcation_flow.cpp
* @brief This is the benchmark test for the bifurcation flow.
* @author Dong Wu
*/
/**
* @brief SPHinXsys Library.
*/
#include "sphinxsys.h"
That gets us all the declarations we need to write a SPHinXsys-using application.
Next we import the SPH namespace,
which includes nearly all of the symbols used by SPHinXsys:
/**
* @brief Namespace cite here.
*/
using namespace SPH;
Now, we provide the parameters for geometric modeling.
/**
* @brief Basic geometry parameters.
*/
Real DL_inlet = 4.0; /**< Inlet channel length. */
Real DL_outlet = 8.0; /**< Outlet channel length. */
Real DH = 2.0; /**< Inlet and outlet channel height. */
Real R = 4.0; /**< Branch radius. */
Real W_upper = 0.8; /**< Upper branch width. */
Real W_under = 1.2; /**< Under branch width. */
Real N = 180; /**< Particle number for creating branch. */
Vec2d insert_circle_center(DL_inlet + R + W_upper, 0.0); /**< Location of the branch center. */
Real resolution_ref = 0.1; /**< Global reference resolution. */
Real DL_sponge = resolution_ref * 20.0; /**< Sponge region to impose inflow condition. */
Real BW = resolution_ref * 4.0; /**< Boundary width, determined by specific layer of boundary particles. */
/** Domain bounds of the system. */
BoundingBox system_domain_bounds(Vec2d(-DL_sponge - BW, -R - W_under - BW),
Vec2d(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, R + W_upper + BW));
Here, particle_spacing_ref gives the reference initial particle spacing.
BW is the size (thickness) of a wall boundary, which is usually 4 times of particle spacing.
DL_sponge is used to define the sponge region for imposing inflow condition.
We give the the coordinates of lower and upper bounds of the domain
in system_domain_bounds
which will be used as the bounds for a mesh used for building cell linked lists.
We also provide parameters for physical modeling, such as material properties of the fluid and physical parameters of the bifurcation flow problem.
/**
* @brief Material properties of the fluid.
*/
Real rho0_f = 1.0; /**< Density. */
Real U_f = 1.0; /**< Characteristic velocity. */
Real c_f = 10.0 * U_f; /**< Speed of sound. */
Real Re = 100.0; /**< Reynolds number. */
Real mu_f = rho0_f * U_f * DH / Re; /**< Dynamics viscosity. */
As we are using a weakly compressible model for imposing incompressibility, the maximum speed in the flow and artificial speed of sound are estimated.
Then, we define the realization of the SPHBody.
First, the geometric shape,
water_block_shape,
is defined form the coordinates based on the geometric parameters.
/**
* @brief define geometry of SPH bodies
*/
/** create a water block shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape1()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape1;
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, 0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper), 0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper), -0.5 * DH));
water_block_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
return water_block_shape1;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape2()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape2;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
water_block_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] + (R + W_upper) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
water_block_shape2.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet, 0.0));
return water_block_shape2;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createWaterBlockShape3()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> water_block_shape3;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
water_block_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + (R + W_under) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] - (R + W_under) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
water_block_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + R + W_under, 0.0));
return water_block_shape3;
}
The createWaterBlockShape1 defines a rectangular shape,
and the createWaterBlockShape2 and createWaterBlockShape3 define the shape of the upper and under semicircle respectively.
Then, the geometric shapes,
inflow_buffer_shape, outer_wall_shape and inner_wall_shape,
are difined.
/** create a water block buffer shape. */
MultiPolygon createInflowBufferShape()
{
std::vector<Vecd> inflow_buffer_shape;
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, 0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(0.0, 0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(0.0, -0.5 * DH));
inflow_buffer_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge, -0.5 * DH));
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(inflow_buffer_shape, ShapeBooleanOps::add);
return multi_polygon;
}
/** create outer wall shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape1()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape1;
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, 0.5 * DH + BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, 0.5 * DH + BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
outer_wall_shape1.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH - BW));
return outer_wall_shape1;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape2()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape2;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
outer_wall_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper + BW) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] + (R + W_upper + BW) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
outer_wall_shape2.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] - (R + W_upper + BW), 0.0));
return outer_wall_shape2;
}
std::vector<Vecd> createOuterWallShape3()
{
//geometry
std::vector<Vecd> outer_wall_shape3;
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; ++i)
{
outer_wall_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + (R + W_under + BW) * cos(i * Pi / N),
insert_circle_center[1] - (R + W_under + BW) * sin(i * Pi / N)));
}
outer_wall_shape3.push_back(Vecd(insert_circle_center[0] + R + W_under + BW, 0.0));
return outer_wall_shape3;
}
/** create inner wall shape */
std::vector<Vecd> createInnerWallShape()
{
std::vector<Vecd> inner_wall_shape;
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, 0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, 0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(DL_inlet + DL_outlet + 2 * (R + W_upper) + BW, -0.5 * DH));
inner_wall_shape.push_back(Vecd(-DL_sponge - BW, -0.5 * DH ));
return inner_wall_shape;
}
The inflow_buffer_shape is used for generating better inflow boundary condition.
After that, we define the fluid body and wall boundary.
/** Fluid body definition */
class WaterBlock : public FluidBody
{
public:
WaterBlock(SPHSystem& system, std::string body_name)
: FluidBody(system, body_name)
{
/** Geomtry definition. */
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape1(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
body_shape_.add<MultiPolygonShape>(multi_polygon);
}
};
/* Definition of the solid body. */
class WallBoundary : public SolidBody
{
public:
WallBoundary(SPHSystem& system, std::string body_name)
: SolidBody(system, body_name, makeShared<SPHAdaptation>(1.15, 1.0))
{
/** Geomtry definition. */
MultiPolygon multi_polygon;
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape1(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createOuterWallShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createInnerWallShape(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape2(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addAPolygon(createWaterBlockShape3(), ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::add);
multi_polygon.addACircle(insert_circle_center, R - BW, 100, ShapeBooleanOps::sub);
MultiPolygonShape multi_polygon_shape(multi_polygon);
body_shape_.add<LevelSetShape>(this, multi_polygon_shape);
}
};
The WaterBlock and WallBoundary,
which are the derived class of FluidBody and SolidBody respectively,
are difined with boolean operation,
such as add and sub.
Then, we define the inflow boundary condition and observation body.
/** Case dependent inflow boundary condition. */
class ParabolicInflow : public fluid_dynamics::InflowBoundaryCondition
{
Real u_ave_, u_ref_, t_ref;
public:
ParabolicInflow(FluidBody &fluid_body, BodyPartByCell &constrained_region)
: InflowBoundaryCondition(fluid_body, constrained_region),
u_ave_(0), u_ref_(1.0), t_ref(20.0) {}
Vecd getTargetVelocity(Vecd& position, Vecd& velocity)
{
Real u = velocity[0];
Real v = velocity[1];
if (position[0] < 0.0) {
u = (-6.0 * position[1] * position[1] / DH / DH + 1.5) * u_ave_;
v = 0.0;
}
return Vecd(u, v);
}
void setupDynamics(Real dt = 0.0) override
{
Real run_time = GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_;
u_ave_ = u_ref_ * 0.5 * (1.0 + sin(Pi * run_time / t_ref - 0.5 * Pi));
}
};
/** fluid observer particle generator */
class FluidObserverParticleGenerator : public ParticleGeneratorDirect
{
public:
FluidObserverParticleGenerator() : ParticleGeneratorDirect()
{
/** A line of measuring points at the entrance of the channel. */
size_t number_observation_pionts = 21;
Real range_of_measure = DH - resolution_ref * 4.0;
Real start_of_measure = resolution_ref * 2.0 - 0.5 * DH;
/** the measureing particles */
for (size_t i = 0; i < number_observation_pionts; ++i)
{
Vec2d point_coordinate(0.0, range_of_measure * Real(i) / Real(number_observation_pionts - 1) + start_of_measure);
positions_volumes_.push_back(std::make_pair(point_coordinate, 0.0));
}
}
};
The ParabolicInflow defines the parabolic velocity field at inflow boundary.
The FluidObserverParticleGenerator defines the observation body
through adding the observation points along the line x = 0.
The observation body obtains data from the body it is observing at and can be used to check the inflow boundary condition.
After all SPHBody s are defined, here comes to the int main() function,
in which the application is defined.
In the first part of main function,
an object of SPHSystem is created,
whether to run the particle relaxation and reload particles,
and whether the computation begins from restart files are checked,
and input/output environment is initialized.
/** Build up the environment of a SPHSystem with global controls. */
SPHSystem system(system_domain_bounds, resolution_ref);
/** Tag for run particle relaxation for the initial body fitted distribution. */
system.run_particle_relaxation_ = false;
/** Tag for computation start with relaxed body fitted particles distribution. */
system.reload_particles_ = true;
/** Tag for computation from restart files. 0: start with initial condition. */
system.restart_step_ = 0;
//handle command line arguments
#ifdef BOOST_AVAILABLE
system.handleCommandlineOptions(ac, av);
#endif
/** output environment. */
In_Output in_output(system);
/**
* @brief Creating body, materials and particles.
*/
WaterBlock water_block(system, "WaterBody");
FluidParticles fluid_particles(water_block, makeShared<WeaklyCompressibleFluid>(rho0_f, c_f, mu_f));
WallBoundary wall_boundary(system, "Wall");
SharedPtr<ParticleGenerator> wall_particle_generator = makeShared<ParticleGeneratorLattice>();
if (!system.run_particle_relaxation_ && system.reload_particles_)
wall_particle_generator = makeShared<ParticleGeneratorReload>(in_output, wall_boundary.getBodyName());
SolidParticles wall_particles(wall_boundary, wall_particle_generator);
ProbeBody fluid_observer(system, "FluidObserver");
ObserverParticles flow_observer_particles(fluid_observer, makeShared<FluidObserverParticleGenerator>());
/**
* @brief Define body relation map.
* The contact map gives the topological connections between the bodies.
* Basically the the range of bodies to build neighbor particle lists.
*/
BodyRelationInner water_block_inner(water_block);
ComplexBodyRelation water_block_complex(water_block, { &wall_boundary });
BodyRelationContact fluid_observer_contact(fluid_observer, { &water_block });
The material, particles and bodies are created for fluid block, wall and observer. Note that, whether the wall particles are reloaded is checked. Then, the collection of topological relations, which specifies for each body the possible interacting bodies, are defined.
After this, the particle relaxation will be run if system.run_particle_relaxation_ = true.
/** Run particle relaxation for body-fitted distribution if chosen. */
if (system.run_particle_relaxation_)
{
/** body topology only for particle relaxation */
BodyRelationInner wall_boundary_inner(wall_boundary);
/**
* @brief Methods used for particle relaxation.
*/
/** Random reset the particle position. */
RandomizePartilePosition random_wall_boundary_particles(wall_boundary);
/** Write the body state to Vtu file. */
BodyStatesRecordingToVtp write_wall_boundary_to_vtp(in_output, { &wall_boundary });
/** Write the particle reload files. */
ReloadParticleIO write_wall_boundary_particle_reload_files(in_output, { &wall_boundary });
/** A Physics relaxation step. */
relax_dynamics::RelaxationStepInner relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner(wall_boundary_inner);
/**
* @brief Particle relaxation starts here.
*/
random_wall_boundary_particles.parallel_exec(0.25);
relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner.surface_bounding_.parallel_exec();
write_wall_boundary_to_vtp.writeToFile(0);
/** relax particles of the insert body. */
int ite_p = 0;
while (ite_p < 1000)
{
relaxation_step_wall_boundary_inner.parallel_exec();
ite_p += 1;
if (ite_p % 200 == 0)
{
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(9) << "Relaxation steps for the inserted body N = " << ite_p << "\n";
write_wall_boundary_to_vtp.writeToFile(ite_p);
}
}
std::cout << "The physics relaxation process of the cylinder finish !" << std::endl;
/** Output results. */
write_wall_boundary_particle_reload_files.writeToFile(0);
return 0;
}
In this way, we can get the initial body-fitted particle distribution. Note that, we only need to run particle relaxation for the solid particles since the fluid partices can flow arond the body-fitted solid particles.
After this, the physical dynamics of system is defined as method classes in the form of particle discretization.
/**
* @brief Methods used for time stepping.
*/
/** Initialize particle acceleration. */
TimeStepInitialization initialize_a_fluid_step(water_block);
/** Evaluation of density by summation approach. */
fluid_dynamics::DensitySummationComplex update_density_by_summation(water_block_complex);
/** Time step size without considering sound wave speed. */
fluid_dynamics::AdvectionTimeStepSize get_fluid_advection_time_step_size(water_block, U_f);
/** Time step size with considering sound wave speed. */
fluid_dynamics::AcousticTimeStepSize get_fluid_time_step_size(water_block);
/** Pressure relaxation using verlet time stepping. */
/** Here, we do not use Riemann solver for pressure as the flow is viscous. */
fluid_dynamics::PressureRelaxationWithWall pressure_relaxation(water_block_complex);
fluid_dynamics::DensityRelaxationRiemannWithWall density_relaxation(water_block_complex);
/** Computing viscous acceleration. */
fluid_dynamics::ViscousAccelerationWithWall viscous_acceleration(water_block_complex);
/** Impose transport velocity. */
fluid_dynamics::TransportVelocityCorrectionComplex transport_velocity_correction(water_block_complex);
/** viscous acceleration and transport velocity correction can be combined because they are independent dynamics. */
CombinedInteractionDynamics viscous_acceleration_and_transport_correction(viscous_acceleration, transport_velocity_correction);
/** Computing vorticity in the flow. */
fluid_dynamics::VorticityInner compute_vorticity(water_block_inner);
/** Inflow boundary condition. */
MultiPolygonShape inflow_buffer_shape(createInflowBufferShape());
BodyRegionByCell inflow_buffer(water_block, "Buffer", inflow_buffer_shape);
ParabolicInflow parabolic_inflow(water_block, inflow_buffer);
/** Periodic BCs in x direction. */
PeriodicConditionInAxisDirectionUsingCellLinkedList periodic_condition(water_block, xAxis);
First, the particle acceleration is initialized to zero. Then, the methods that will used for multiple times are defined. They are the SPH algorithms for the fluid dynamics and the time step criteria. Note that, the transport velocity is imposed to address the tensile instability which cases void region or particle dumping. After that, the calculation of vorticity and inflow and periodic boundary conditions are difined.
After the dynamics, we also define the outputs, including the particle states, restart files and observations.
/**
* @brief Define the methods for I/O operations and observations of the simulation.
*/
BodyStatesRecordingToVtp write_real_body_states(in_output, system.real_bodies_);
RestartIO restart_io(in_output, system.real_bodies_);
ObservedQuantityRecording<Vecd> write_fluid_velocity("Velocity", in_output, fluid_observer_contact);
The Vtp files can be read directly by the open-source visualization code ParaView.
You also have the option to save the files in Tecplot format.
The observation data are written in simple data format
and the restart files are in XML data format.
Before the computation, we need to prepare the simulation with the cell linked list, configuration and the wall normal direction.
/**
* @brief Prepare the simulation with cell linked list, configuration
* and case specified initial condition if necessary.
*/
/** initialize cell linked lists for all bodies. */
system.initializeSystemCellLinkedLists();
/** periodic condition applied after the mesh cell linked list build up
* but before the configuration build up. */
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
/** initialize configurations for all bodies. */
system.initializeSystemConfigurations();
/** computing surface normal direction for the wall. */
wall_particles.initializeNormalDirectionFromBodyShape();
Finally, the time stepping will almost start. However, if the computation begin from restart files. The system will be reset.
/**
* @brief Load restart file if necessary.
*/
if (system.restart_step_ != 0)
{
GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ = restart_io.readRestartFiles(system.restart_step_);
water_block.updateCellLinkedList();
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
/** one need update configuration after periodic condition. */
water_block_complex.updateConfiguration();
}
Note that, because the particles have been moved in the previous simulation, one need to update the cell-linked list and particle configuration.
The basic control parameter for the simulation is defined, such as the restart file, output frequency, total simulation time, interval for writing output files, etc.
/**
* @brief Setup for time-stepping control
*/
size_t number_of_iterations = system.restart_step_;
int screen_output_interval = 100;
int restart_output_interval = screen_output_interval * 10;
Real End_Time = 100.0; /**< End time. */
Real D_Time = End_Time / 100.0; /**< time stamps for output. */
Real Dt = 0.0; /**< Default advection time step sizes for fluid. */
Real dt = 0.0; /**< Default acoustic time step sizes for fluid. */
size_t inner_ite_dt = 0;
/** Statistics for computing time. */
tick_count t1 = tick_count::now();
tick_count::interval_t interval;
/** First output before the main loop. */
write_real_body_states.writeToFile();
write_fluid_velocity.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
Also the statistic for computation time is initialized and the initial body states and data are outputed.
Here comes the time-stepping loops. The computation is carried out with a dual-criteria time-stepping scheme, as discussed in SPHinXsys’s theory section.
/**
* @brief Main loop starts here.
*/
while (GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ < End_Time)
{
Real integration_time = 0.0;
/** Integrate time (loop) until the next output time. */
while (integration_time < D_Time)
{
initialize_a_fluid_step.parallel_exec();
Dt = get_fluid_advection_time_step_size.parallel_exec();
update_density_by_summation.parallel_exec();
viscous_acceleration_and_transport_correction.parallel_exec(Dt);
inner_ite_dt = 0;
Real relaxation_time = 0.0;
while (relaxation_time < Dt)
{
dt = SMIN(get_fluid_time_step_size.parallel_exec(), Dt);
/** Fluid pressure relaxation */
pressure_relaxation.parallel_exec(dt);
/** Fluid density relaxation */
density_relaxation.parallel_exec(dt);
relaxation_time += dt;
integration_time += dt;
GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_ += dt;
parabolic_inflow.parallel_exec();
inner_ite_dt++;
}
if (number_of_iterations % screen_output_interval == 0)
{
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(9) << "N=" << number_of_iterations << " Time = "
<< GlobalStaticVariables::physical_time_
<< " Dt = " << Dt << " Dt / dt = " << inner_ite_dt << "\n";
if (number_of_iterations % restart_output_interval == 0 && number_of_iterations != system.restart_step_)
restart_io.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
}
number_of_iterations++;
/** Water block configuration and periodic condition. */
periodic_condition.bounding_.parallel_exec();
water_block.updateCellLinkedList();
periodic_condition.update_cell_linked_list_.parallel_exec();
water_block_complex.updateConfiguration();
}
tick_count t2 = tick_count::now();
/** write run-time observation into file */
compute_vorticity.parallel_exec();
write_real_body_states.writeToFile();
fluid_observer_contact.updateConfiguration();
write_fluid_velocity.writeToFile(number_of_iterations);
tick_count t3 = tick_count::now();
interval += t3 - t2;
}
tick_count t4 = tick_count::now();
tick_count::interval_t tt;
tt = t4 - t1 - interval;
std::cout << "Total wall time for computation: " << tt.seconds() << " seconds." << std::endl;
return 0;
During the looping outputs are scheduled. On screen output will be the number of time steps, the current physical time, the advection time-step size and the number of acoustic time steps in an advection time-step size. After the simulation is terminated, the statistics of computation time are output on the screen.
